
Initiatives for SDGs and carbon neutrality, “No need to wait” – How to reduce power consumption
-
- Category:
- COLUMN
-
- Date:
- Apr.30.2024
Interview with Kenkichi Abe, General manager, Solution Strategy Department at Kawashima Packaging Machinery Ltd.
Measures for SDGs/carbon neutrality and the future led by the latest environmental technology
Changes in consumer awareness and the market environment are now spreading across the world as a major trend. Environmental awareness of the public has grown rapidly over the past few years, resulting in SDGs as the fruition. Corporate management is under great pressure from external factors, such as rising energy costs and a competitive environment that makes it difficult to differentiate. How can we continue to grow sustainably in this era of dramatic change?
Kenkichi Abe, head of the Packaging Solutions Strategy Office, will talk about the response of Kawashima Packaging Machinery Ltd. to SDGs and carbon neutrality, the progress of the latest environmental technology, and the innovative packaging technology that will lead the future and solve the challenges faced by food manufacturing sites.

Kenkichi Abe, General manager, Solution Strategy Department at Kawashima Packaging Machinery Ltd.
Initiatives for SDGs and carbon neutrality “No need to wait” – How to reduce power consumption
What it takes to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and achieve renewable energy transition
>SDGs, which are commonly established as sustainable development goals nowadays, were considered only by a few major corporations several years ago. In recent years, the importance of SDGs has been rapidly recognized and discussed. What kind of initiatives are being actively undertaken in the food industry?
Abe: The recognition of SDGs has gradually spread since they were adopted by the United Nations in 2015, and in the past few years they have suddenly become a phenomenon that people are interested in. There are many responsibilities that companies must fulfil for the SDGs, in which carbon neutrality in particular, is well recognized by food manufactures as an important issue that must be addressed urgently.
>What kind of efforts are you making towards carbon neutrality?
Abe: Carbon neutrality refers to efforts to reduce greenhouse gases such as CO2 and chlorofluorocarbons, and offset them with the CO2 consumed by forests to virtually eliminate them. Japan has announced that it will achieve carbon neutrality nationwide by 2050, and its roadmap aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 46% by 2030 compared to 2013, and also try to reach the highest level of 50% as a challenge. In addition, efforts to achieve carbon neutrality include increasing the rate of renewable energy, about which specific goals to be achieved by 2030 are also considered. We have decided to reduce the use of fossil fuels, which we have been using mainly, and to steadily increase the use of natural energy.
>What kind of roadmap is being laid out to improve the renewable energy rate?
Abe: Electricity in Japan can be broadly divided into three types: fossil fuels, natural energy (wind, water, solar, etc.), and nuclear power. As of 2020, fossil fuels are the most commonly used fuel, accounting for approximately 75% of the total consumption. The proportion of natural energy is 20.8%. We need to increase this to 38%.
>When we talk about natural energy, there are various types such as wind power and water power. It seems that solar energy is most commonly used.
Abe: In order to promote renewable energy such as solar power generation, the government has established a feed-in tariff system for renewable energy, in which generated electricity is purchased at a fixed price for a certain period of time. This topic has been widely covered in the media, so many people may have heard of it. There is a renewable energy power generation promotion levy (renewable energy levy) as a mechanism to maintain this purchase system. All electricity users now have to pay the renewable energy purchase fees originally paid by power companies. Currently, Japan’s renewable energy levy accounts for approximately 11% of electricity fees. Even though electricity fees are already high, renewable energy levies are likely to increase further in the future. Furthermore, assuming that the Japanese economy continues to grow, the Bank of Japan estimates that Japan’s GDP will reach 660 trillion yen in 2030.
>As the economy grows, electricity consumption will inevitably increase.
Abe: Currently, the automobile industry is moving away from gasoline and moving towards EVs (electric vehicles) at an accelerated pace, so it is expected that electricity consumption will continue to increase. Regarding raising the renewable energy rate, we have been able to raise it to 21% in 2021. If everything goes smoothly, I feel like we will be able to achieve our goal of generating 38% of our electricity by renewable energy by 2030, but considering that overall electricity consumption is increasing, it is expected that increasing the renewable energy rate will become increasingly difficult in the future. I think we need to seriously address the issue of how to reduce electricity consumption and reduce CO2 and other greenhouse gas emissions.
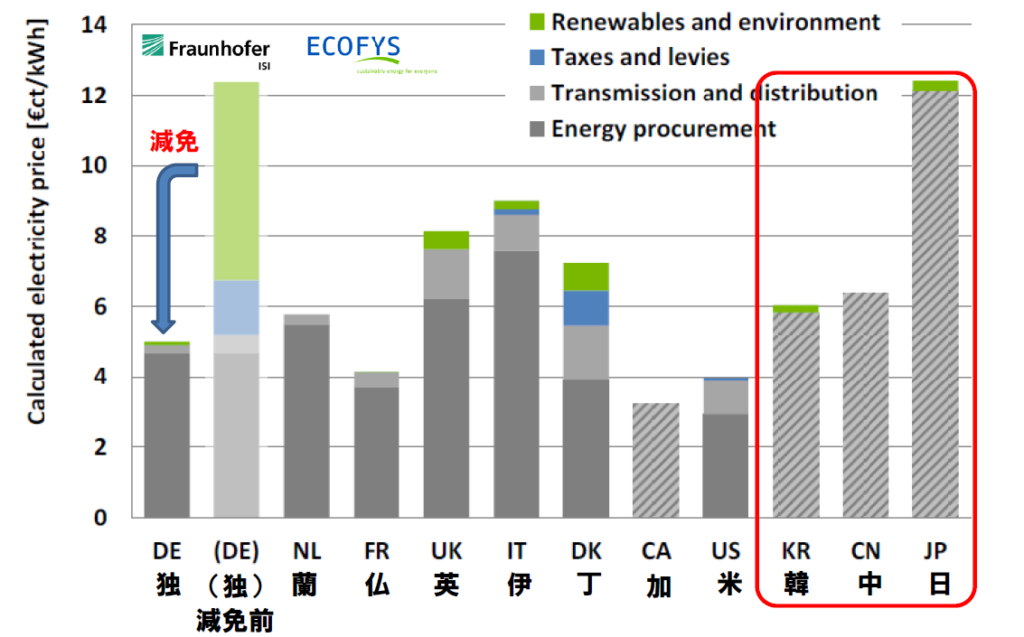
Figure 1: International comparison graph of electricity rates for power-intensive industries (Source: Institute for International Environmental Economics, specified non-profit organization)
The challenge of packaging professional KAWASHIMA
>What do you think Kawashima Packaging Machinery Ltd. can actually do to support the SDGs initiatives of food manufacturers?
Abe: Kawashima Packaging Machinery Ltd. is currently working on the following three main initiatives.
◆Improvement of packaging machine capacity
◆Reducing the power consumption of “air compressors”
◆ Switching to a sealing method that saves power during film crimping
The first initiative I would like to share with you is the thorough power saving by improving the performance of Kawashima Packaging Machinery Ltd.’s packaging machines. The food industry has equipment that uses large amounts of electricity, such as air conditioners, boilers, and fryers. Packaging machines are one such device that consumes large amount of electricity, so packaging machines that operate with lower power consumption are sure to become more important in the future. For example, to pack 120 products using Kawashima Packaging Machinery Ltd.’s vertical pillow packaging machine with a conventional speed of 60rpm (*rpm is the number of products that can be wrapped in 1 minute. 60rpm is the number of products that can be wrapped in 1 minute.), two packaging machines were needed for the process. In that case, the power consumption per unit is 0.84 kilowatts. On the other hand, the power consumption of one 120 rpm machine is 0.95 kilowatts. At 150rpm, the consumption is 1.0kW. Doubling the capacity does not mean that the power consumption will also double. Even if a packaging machine can package twice the amount at once, the difference in power consumption is less than 1 kilowatt. If power consumption decreases, the carbon dioxide emissions will also decrease, and thus lowering electricity bills. Kawashima Packaging Machinery Ltd.’s latest vertical pillow packaging machine has a maximum packaging capacity of 200 rpm, making it possible to complete a large amount of packaging in a short time and with lower power consumption.
>Improving the performance of packaging machines is one of the initiatives that can help reduce the electricity costs of client companies. By combining two machines into one, you can save space. The cleaning time will be cut in half, and the number of operators can be reduced from two to one. In addition to simply reducing power consumption, there are many other benefits.
Abe: The second merit is to reduce the number of air cylinders used and develop an airless packaging machine. Industrial machines often use a mechanism called an “air cylinder” that compresses air into a piston to push and pull it. They have the great advantage of being simpler and costing less than a motor, but they require an air generator called a compressor, which consumes a considerable amount of power. In some cases, the power consumption of air compressors is so high that they can account for as much as 20% of the entire factory’s power consumption. You cannot reduce the overall power consumption unless you consider not only the power consumption of the packaging machine itself, but also the power used to generate the air. At Kawashima Packaging Machinery Ltd., we have developed a packaging machine that uses a motor instead of the conventional air drive, whose power consumption is 0.94 kilowatts. The use of a motor consumes more power than our conventional packaging machines, but compared to the additional power consumed to drive the air compressor, considerable power savings can be achieved. In the future, we would like to increase the number of airless machines and propose optimal solutions to our customers.
>In addition to power saving, are there any other benefits of airlessness?
Abe: As many of you probably know, the compressor that generates air makes a very loud noise.
For this reason, the compressor is usually located in a separate building from the packaging machine, and air is sent to the packaging machine via piping. If you go airless, you won’t need a compressor, and the noise caused by the compressor will disappear. In addition, there is no need for piping to send air, and thus the nylon tubes that were used to send air from a separate building to each device are no longer needed. Eliminating piping and nylon tubes will make the factory more organized, and there will be no need for a room for compressors, allowing the factory to be used more freely. Since piping and nylon tubes are consumable items, the amount of plastic waste is reduced, thus contributing to the elimination of plastics.

In-house power generation for packaging machines
>I heard that packaging machine has various parts. Which part uses the most electricity?
Abe: It is the part where the packaging material is glued.
To make a bag from a single sheet of film, food packaging uses heat to seal the bottom, top, sides, and back of the bag. Therefore, among the various parts of the packaging machine, the part that uses the most electricity is the part that glues the packaging materials together. There are various methods of sealing, but the one that has been commonly used is a method of sealing by combining a hot iron block called a heater block, which requires maintaining a high temperature of about 130 to 160 degrees Celsius on average. For this reason, Kawashima Packaging Machinery Ltd. is considering ways to save energy during this sealing process. Currently, a possible method of sealing is to use ultrasonic waves. By applying ultrasonic vibration and pressure, the adhesive surfaces are instantly melted and bonded. Ultrasonic sealing is said to reduce power consumption by up to 75% when compared to heat sealing.
>That’s amazing. If it can reduce power consumption so significantly, why hasn’t it been used more often?
Abe: In the case of the ultrasonic sealing method, parts that need not to be glued were also glued, weakening the strength of those parts and making it easier for holes to form. Another downside was that the ink in the sealed area could be blown away by vibrations, affecting the package design. However, ultrasonic seal units have also evolved overtime. We have reconsidered sealing methods from the perspective of carbon neutrality and believe that the power saving benefits of using ultrasonic seals are significant. We are currently testing from various perspectives, considering how to overcome demerits, and proceeding with development. The demerit of easily forming holes is especially lethal for packaging machines that process food, and therefore, we are testing and alleviating this problem. Due to the disadvantage of the ink peeling off from the back of the bag, in the past, ultrasonic sealing method was rejected for the bad appearance of the packaging it made. But an increasing number of companies are thinking that “If we can reduce power consumption and contribute to carbon neutrality, we are willing to accept the demerits. In fact, we should work on packaging designs that take advantage of this demerit.”
> User awareness is also changing. Compared to heat sealing, ultrasonic sealing consumes significantly less power.
Abe: Although the initial cost is high, ultrasonic sealing method’s overall cost is much lower. For our customers, there are more benefits than drawbacks, so we are actively considering increasing the use of ultrasonic sealing methods. In addition, we are currently considering the technology that would further reduce the power consumption of packaging machines by reusing the “heat” produced through operation as electricity. It moves itself with its own heat. One day, we may be able to offer a packaging machine that works like a perpetual motion machine.
(To be continued)
-

-
CEO Blog-SPECIAL INTERVIEW 04 Part 2 -More important continuation than assessment.Because you can like yourself, you can make your partner happy as well-
-

-
The latest efforts in environmentally friendly packaging materials and the ability of advanced packaging materials to enhance product branding


